facilitated diffusion vs protein chanel | facilitated diffusion with carrier proteins facilitated diffusion vs protein chanel Learn how molecules move across membranes by passive diffusion, . LV Carpets specializes in carpet cleaning, tile and grout cleaning, carpet pet stain removal and area rug cleaning in Las Vegas. From small condos to large homes, you can count on us for the best carpet cleaning service. Contact us today to schedule your carpet cleaning service in Las Vegas.
0 · which statements describe facilitated diffusion
1 · which shows facilitated diffusion
2 · what does facilitated diffusion require
3 · molecules that use facilitated diffusion
4 · facilitated diffusion with carrier proteins
5 · facilitated diffusion via protein channel
6 · facilitated diffusion through channel protein
7 · does facilitated diffusion require atp
4. Periksa hardware LV. Cara mudah untuk melihat apakah tas merek mewah itu asli adalah dengan melihat hardware-nya, seperti potongan aksen atau tarikan resleting. Pada tas vintage yang tak lekang oleh waktu seperti tas Louis Vuitton Neverfull, Anda dapat segera mengetahui apakah itu imitasi.
Facilitated diffusion is the passive transport of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. Learn about channel proteins, gated channel proteins, and carrier proteins that are involved in facilitated diffusion.Learn how molecules move across membranes by passive diffusion, .
Learn how solutes can move across a membrane by passive diffusion, driven .
fitbit clone watch
All channel proteins and many carrier proteins allow solutes to cross the membrane only passively (“downhill”), a process called passive transport, or facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion is a form of passive transport involving the movement of molecules along their concentration gradient, guided by proteins. Learn how facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion, and see examples .Facilitated diffusion is the passive transport of molecules or ions across a membrane via specific proteins. Learn how it differs from simple diffusion, how it regulates metabolic processes, and how it applies to transcription factors, . Learn about facilitated diffusion, a type of passive transport that requires membrane proteins for charged and large polar molecules. Find out the differences between carrier proteins, ion channels, and aquaporins, and how .
Learn how solutes can move across a membrane by passive diffusion, driven by concentration gradient, or by facilitated diffusion, with the help of carrier proteins or channels. Explore the factors that affect the rate of .
which statements describe facilitated diffusion
Channel proteins carry out the majority of facilitated diffusion. While the chemicals are still moving in the direction of their concentration (from high to low), they are given a passageway through the cell membrane.Facilitated diffusion is the passive transport of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. Learn about channel proteins, gated channel proteins, and carrier proteins that are involved in facilitated diffusion.
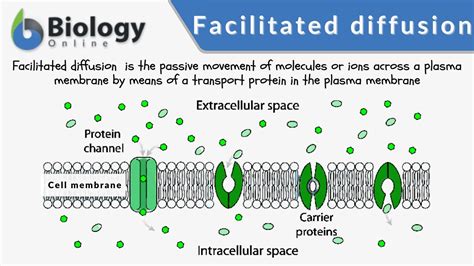
Learn how molecules move across membranes by passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. Facilitated diffusion is the spontaneous passage of molecules or ions across membranes through specific transmembrane proteins, such as carrier proteins and channel proteins. Facilitated diffusion: Transmembrane proteins create a water-filled pore through which ions and some small hydrophilic molecules can pass by diffusion. The channels can be opened (or closed) according to the needs of the cell.
Facilitated diffusion is a form of passive transport that involves molecules diffusing across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. Learn how facilitated diffusion works, what types of molecules it affects, and how it differs from simple diffusion.
All channel proteins and many carrier proteins allow solutes to cross the membrane only passively (“downhill”), a process called passive transport, or facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion is a form of passive transport involving the movement of molecules along their concentration gradient, guided by proteins. Learn how facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion, and see examples of carrier and channel proteins.
Facilitated diffusion is the passive transport of molecules or ions across a membrane via specific proteins. Learn how it differs from simple diffusion, how it regulates metabolic processes, and how it applies to transcription factors, oxygen, and chromatin.
Learn about facilitated diffusion, a type of passive transport that requires membrane proteins for charged and large polar molecules. Find out the differences between carrier proteins, ion channels, and aquaporins, and how they affect cellular processes. Learn how solutes can move across a membrane by passive diffusion, driven by concentration gradient, or by facilitated diffusion, with the help of carrier proteins or channels. Explore the factors that affect the rate of diffusion and . Channel proteins carry out the majority of facilitated diffusion. While the chemicals are still moving in the direction of their concentration (from high to low), they are given a passageway through the cell membrane.
Facilitated diffusion is the passive transport of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. Learn about channel proteins, gated channel proteins, and carrier proteins that are involved in facilitated diffusion.Learn how molecules move across membranes by passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. Facilitated diffusion is the spontaneous passage of molecules or ions across membranes through specific transmembrane proteins, such as carrier proteins and channel proteins.
episode ii attack of the clones putlocker watch free online
Facilitated diffusion: Transmembrane proteins create a water-filled pore through which ions and some small hydrophilic molecules can pass by diffusion. The channels can be opened (or closed) according to the needs of the cell.Facilitated diffusion is a form of passive transport that involves molecules diffusing across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. Learn how facilitated diffusion works, what types of molecules it affects, and how it differs from simple diffusion.All channel proteins and many carrier proteins allow solutes to cross the membrane only passively (“downhill”), a process called passive transport, or facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion is a form of passive transport involving the movement of molecules along their concentration gradient, guided by proteins. Learn how facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion, and see examples of carrier and channel proteins.

Facilitated diffusion is the passive transport of molecules or ions across a membrane via specific proteins. Learn how it differs from simple diffusion, how it regulates metabolic processes, and how it applies to transcription factors, oxygen, and chromatin. Learn about facilitated diffusion, a type of passive transport that requires membrane proteins for charged and large polar molecules. Find out the differences between carrier proteins, ion channels, and aquaporins, and how they affect cellular processes.
which shows facilitated diffusion
what does facilitated diffusion require
Learn how solutes can move across a membrane by passive diffusion, driven by concentration gradient, or by facilitated diffusion, with the help of carrier proteins or channels. Explore the factors that affect the rate of diffusion and .

death watch clone wars episode
molecules that use facilitated diffusion
Health Topics. Cardiomyopathy. What is cardiomyopathy in adults? Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that makes it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body. The various types of the disease have many causes, signs and symptoms as well as treatments.
facilitated diffusion vs protein chanel|facilitated diffusion with carrier proteins